In early 2024, Roku faced a significant data breach that affected over 15,000 user accounts between December 28, 2023, and February 21, 2024. Unauthorized access, reportedly through third-party obtained credentials, exposed sensitive information and left users vulnerable.
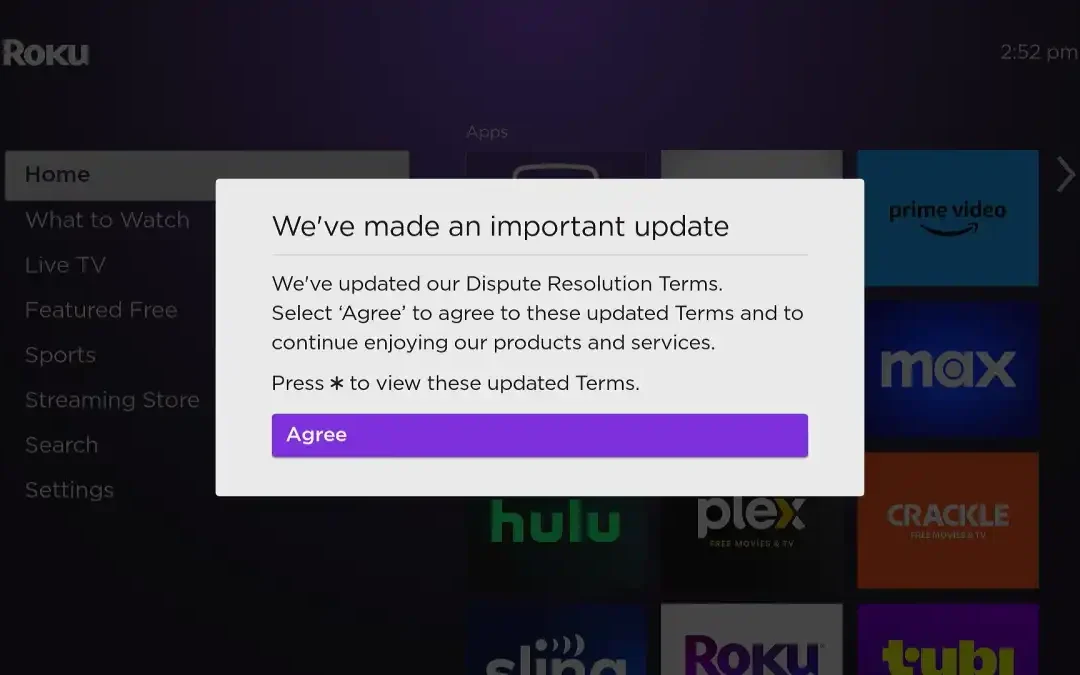
Following the breach, Roku updated its Terms of Service, introducing a forced arbitration clause. The new terms required users to accept these conditions in order to continue using their Roku TVs and streaming devices. This effectively disabled devices for users who did not immediately agree.
Forced Arbitration and Legal Implications
The updated Terms of Service included provisions that prevent users from suing Roku or joining class-action lawsuits. Instead, all disputes would have to be resolved through individual arbitration. Critics argue that forced arbitration clauses heavily favor companies and limit consumers’ legal recourse, raising serious ethical and legal concerns.
User Backlash
Roku users reacted strongly on social media and forums, describing the move as coercive. Many reported feeling “trapped,” with their devices rendered unusable until they agreed to the new terms. The backlash highlights frustration with companies that alter post-purchase terms in ways that directly affect device functionality.
Roku did offer an opt-out option for the forced arbitration clause, allowing users to send a written notice to Roku’s General Counsel within 30 days. However, this process was criticized as cumbersome and not easily accessible for the average consumer.
Broader Implications
This situation underscores the tension between corporate control and consumer rights, particularly when companies introduce post-purchase terms that affect the usability of already-purchased products. Forced arbitration clauses continue to spark debate over fairness, transparency, and the ability of consumers to protect themselves legally.
As the story develops, it serves as a cautionary tale for users to carefully review the terms of service and for lawmakers to consider the broader implications of post-purchase changes in consumer products.

This is a real victory for accessibility and dignity. No one should have to wait months to fix essential mobility…
Throwing away millions of working PCs isn’t innovation, it’s waste. Microsoft needs to rethink its upgrade strategy.
I understand companies want recurring revenue, but pushing ads on high-end appliances feels like crossing a line. Customers paying premium…