On October 14, 2025, Microsoft officially ended support for Windows 10, leaving approximately 400 million users, about 40% of all Windows users, without critical security updates, patches, or technical assistance. This move has sparked concerns about forced obsolescence and increased electronic waste, particularly as many of these users cannot upgrade to Windows 11 due to stringent hardware requirements.
The Windows 10 End-of-Life Transition
Microsoft’s decision to cease support for Windows 10 was part of its broader strategy to push users toward Windows 11. While the operating system will continue to function, the lack of updates exposes systems to potential security vulnerabilities. Users can enroll in Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates (ESU) program to receive critical updates until October 13, 2026, but this comes at an additional cost.
Windows 11’s Strict Hardware Requirements
Windows 11 introduced several new hardware requirements, including:
- A compatible 64-bit processor
- 4 GB of RAM
- 64 GB of storage
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0
- Secure Boot capability
These requirements have rendered many older PCs incompatible with Windows 11, forcing users to either upgrade their hardware or continue using unsupported systems.
Environmental and Social Implications
The combination of Windows 10’s end-of-life and Windows 11’s stringent hardware requirements has led to concerns about increased electronic waste. Critics argue that this planned obsolescence disproportionately affects low-income users and small businesses, widening the digital divide. Organizations like the Public Interest Research Group (PIRG) are advocating for Microsoft to extend support for Windows 10 and reconsider the hardware requirements for Windows 11.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s transition from Windows 10 to Windows 11 has left millions of users in a challenging position. Without affordable upgrade options, many are faced with the prospect of using unsupported systems or incurring additional costs for new hardware. This situation underscores the need for more inclusive technology policies that consider the diverse circumstances of all users.

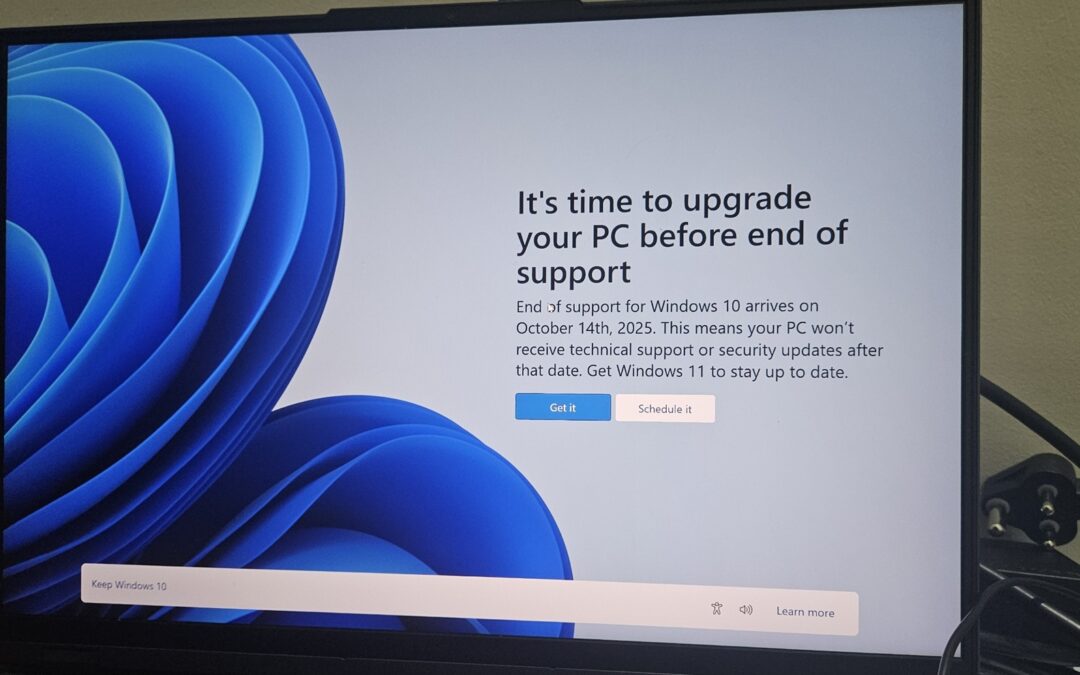
Throwing away millions of working PCs isn’t innovation, it’s waste. Microsoft needs to rethink its upgrade strategy.